Digital Currency in India: How it Works? Benefits Explained
Table of Contents
What is digital currency?
In today’s fast-paced digital age, the concept of Digital Currency In India has taken on a new dimension. It is also known as virtual currency or electronic money, has emerged as a transformative financial phenomenon that has captured the attention of individuals, businesses, and governments across the globe. With its potential to revolutionize transactions and value storage, it is very useful for people to gain an understanding of this exciting Digital Currency In India. In this article, we will understand the concept of Digital Currency In India, and explain its definition, functionality, and the numerous advantages it offers. Whether you’re a tech-savvy enthusiast or someone curious about the potential implications.
Digital currency refers to virtual or electronic money that exists solely in digital form. Unlike traditional physical cash or conventional banking systems, the digital currency operates independently, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries. It utilizes advanced technologies to secure and verify transactions, providing a level of autonomy and convenience.
.
Digital Currency in India
Digital Currency in India has been a topic of increasing interest and discussion in recent years. As the world accepts the digital revolution, India, with its vast population and growing digital infrastructure, has also begun to explore the potential of Digital Currency In India. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has been closely monitoring and studying the feasibility of introducing a central bank digital currency (CBDC) in the country. A CBDC is a digital version of the Indian rupee, providing a secure and efficient medium of exchange for transactions.
Digital currency enhances financial inclusion, streamlines transactions, and provides greater transparency in the financial ecosystem. As the country accepts the possibilities of digital currency, it is essential to address regulatory concerns, ensure data security, and create awareness among the general public about the benefits and responsible usage of digital currency. The future of digital currency in India holds tremendous promise, paving the way for a more digital and inclusive economy.
The Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) gives the promise to the bearer “I PROMISE TO PAY THE BEARER THE SUM OF (ex. ONE HUNDRED) RUPEES” just like written on our physical currency notes. RBI is issuing it in the same denominations that paper currency or physical notes and coins are currently issued ex. Rs. 2000/-, Rs. 500/-, Rs. 100/-, Rs. 50/-, Rs. 20/- etc. (RBI Notification)
Central Bank Digital Currency
“Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)” is the official name of Digital Currency or Digital Rupee in India. Furthermore, Digital Currency is a sovereign currency just like our physical notes and coins. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) is an emerging concept that has gained significant attention in the context of digital currency in India. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has been actively exploring the possibility of introducing a CBDC, which would be a digital version of the Indian rupee. A CBDC would be issued and regulated by the central bank, offering a secure and efficient digital payment system for individuals and businesses. With the potential to revolutionize the financial landscape, a CBDC in India could streamline transactions, promote financial inclusion, and enhance the overall efficiency of the monetary system.
While the implementation of a CBDC requires careful consideration and addressing regulatory aspects, the introduction of digital currency through a CBDC holds immense potential to transform the way transactions are conducted and empower individuals with greater financial access and convenience. The development of a CBDC in India signifies a progressive step towards a digital economy and reinforces the country’s commitment to embracing technological advancements in the financial sector.
Participant Bank in Digital Currency in India.
Eight banks have been identified for the first phase to participate in this pilot project of Digital Currency.
- The first phase will begin with four banks, that is State Bank of India, ICICI Bank, Yes Bank, and IDFC First Bank in four cities across the country.
- In the Second Phase Four more banks, that is Bank of Baroda, Union Bank of India, HDFC Bank, and Kotak Mahindra Bank will join.
After successful testing, analysis and results this will be available in all the banks.
How to buy it? and How Digital Currency Works?
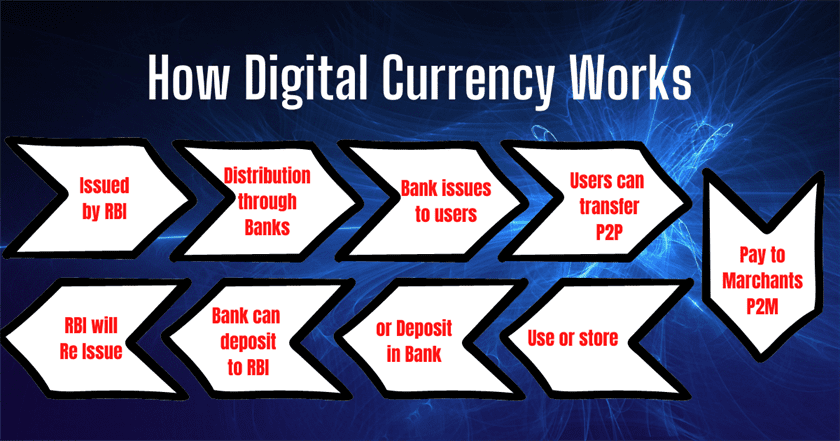
Digital Currency will be issued by RBI and available through banks. Account holders will be able to transact with Digital Currency through a digital wallet offered by the participating banks and stored on mobile phones/devices.
Transactions can be both Person to Person (P2P) and Person to Merchant (P2M). Payments to merchants can be made using QR codes displayed at merchant locations just like UPI.
When Digital Currency is available in my City?
The pilot project initially covered four cities, that is Mumbai, New Delhi, Bengaluru, and Bhubaneswar and later extended to Ahmedabad, Gangtok, Guwahati, Hyderabad, Indore, Kochi, Lucknow, Patna, and Shimla. It will expand gradually to include more banks, users, and locations after the analysis of the pilot project.
In this pilot project, RBI will test the robustness of the entire process of digital rupee creation, distribution, and retail usage in real-time. Different features and applications of the Digital Currency token and architecture will be tested in future pilots, based on the learnings from this pilot.
Features of Digital Currency in India
1. Financial Inclusion: Digital currency in India has the potential to promote financial inclusion by providing access to financial services for the unbanked and underbanked populations. It allows individuals to participate in the formal economy and enjoy basic financial services, regardless of their geographic location or socioeconomic status.
2. Faster and Cost-effective Transactions: Digital currency in India enables near-instantaneous transactions at significantly lower costs compared to traditional banking systems. This speed and efficiency simplify financial transactions, making it easier and more affordable to send and receive payments, both domestically and internationally.
3. Transparency and Accountability: Digital currency transactions in India are recorded on a decentralized ledger, known as a blockchain, which ensures transparency and accountability. This immutable record of transactions fosters trust among users, as every transaction can be verified and audited.
4. Enhanced Security: It utilizes advanced cryptographic protocols to secure transactions. These protocols ensure that each transaction is authenticated and cannot be tampered with, reducing the risk of fraud or unauthorized access to personal financial information.
5. Data Privacy: Digital currency in India prioritizes data security and privacy. While transactions are recorded on a public ledger, personal information is not directly linked to the transactions, preserving the privacy of individuals and protecting their financial data.
6. Global Accessibility: Digital currency in India transcends geographic boundaries, allowing individuals to make cross-border transactions seamlessly. It eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces the complexity and costs associated with traditional international transfers.
7. Technological Advancements: Digital currency embraces technological advancements, such as mobile banking and digital wallets, to provide convenient and user-friendly ways to store and transact digital currency. These technological innovations enhance the accessibility and usability of digital currency for individuals and businesses.
8. Economic Efficiency: Digital currency in India has the potential to improve the overall efficiency of the economy by reducing the reliance on physical cash, streamlining financial processes, and enabling faster economic transactions.
9. Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Digital currency in India fosters innovation and entrepreneurship by providing a conducive environment for the development of innovative financial technologies and services. It opens up new opportunities for startups and businesses to create innovative solutions that leverage digital currency.
10. Government Digitization Efforts: Digital currency in India aligns with the government’s vision of a digital and cashless economy. It supports the digitization efforts undertaken by the government, encouraging the use of digital payments and reducing the dependence on cash transactions.
Types of Digital Currency in India
RBI’s Central Bank Digital Currency is classified into two types Retail (CBDC-R) and Wholesale (CBDC-W)
- Central Bank Digital Currency – Retail (CBDC-R): Retail Digital Currency can be used by all including the private sector, non-financial consumers, and businesses. This Digital Currency version of cash is primarily meant for retail transactions. Central Bank Digital Currency can provide access to safe money for payment and settlement as it is a direct liability of the central bank.
- Central Bank Digital Currency – Wholesale (CBDC-W): Wholesale Digital Currency is designed for restricted access to select financial institutions. It is designed for the settlement of interbank transfers and related wholesale transactions.
CBDC Wholesale has the potential to transform settlement systems for financial transactions and make them more efficient and secure which is equally important.
Difference Between Digital Currency Vs Digital Money
| Digital currency | Digital Money |
| Available like Hard Cash | Money Deposited in Bank |
| Can be Transferred by Token System | Can be Transferred by UPI, NEFT, RTGS |
| Do not earn Interest | Earn Interest |
| Liability of RBI | Liability of Commercial Banks |
| No need for a bank account to use | Need a Bank account to use |
Difference Between Digital Currency Vs Crypto Currency
| Digital currency | Crypto Currency |
| Legal tender | Not a legal tender |
| Value is fixed | Highly Volatile |
| Have Sovereign Guarantee | No any Guarantee |
| Issued by RBI | Issued by Blockchain Technology |
| Issued through Banks | Issued through Crypto Traders |
Difference Between Digital Currency Vs UPI
| Digital currency | UPI |
| Money Available in Token form | Money available in Bank account |
| Direct real-time payment | Real-time payment through bank |
| Regulated by RBI | Regulated by NPCI |
| Person-to-Person or Marchant Transfer | Bank-to-Bank Transfer |
| Actual Money | Its a medium to transfer Money |
Advantages of Digital Currency in India
1. Financial Inclusion: Digital currency in India promotes financial inclusion by providing access to financial services for the unbanked and underbanked populations. It enables individuals without traditional banking facilities to participate in the formal economy, opening up opportunities for economic empowerment.
2. Lower Transaction Costs: It offers lower transaction costs compared to traditional banking systems. With reduced fees and fewer intermediaries involved, digital currency transactions are more cost-effective, benefiting both individuals and businesses.
3. Faster Transactions: Digital currency in India enables near-instantaneous transactions, eliminating the need for lengthy processing times associated with traditional banking systems. This speed and efficiency make digital currency a convenient and time-saving payment method.
4. Increased Security: It utilize advanced cryptographic techniques to secure transactions. This enhances the security of financial transactions, protecting users from fraud and unauthorized access to their funds.
5. Transparency and Accountability: Digital currency transactions in India are recorded on a decentralized public ledger, providing transparency and accountability. This transparent record of transactions reduces the risk of corruption and promotes trust among users.
6. Global Accessibility: Digital currency in India transcends geographical boundaries, enabling seamless cross-border transactions. It eliminates the need for currency conversions and reduces the complexity of international transfers, making it convenient for individuals and businesses operating on a global scale.
7. Privacy Protection: Digital currency in India prioritizes privacy protection. While transactions are recorded on a public ledger, users can maintain a level of privacy as personal information is not directly linked to transactions, ensuring confidentiality.
8. Technological Innovation: It encourages technological innovation by providing a platform for the development of new financial technologies and services. This fosters entrepreneurship and supports the growth of the digital economy in the country.
9. Reduced Cash Dependency: Digital currency in India reduces reliance on physical cash, contributing to the government’s vision of a cashless economy. It promotes digital payments and financial digitization, leading to greater convenience and efficiency in transactions.
10. Financial Empowerment: Digital currency in India empowers individuals to have greater control over their finances. It provides access to a range of financial services, such as savings, loans, and investments, allowing individuals to manage their funds more effectively and make informed financial decisions.
Disadvantages of Digital Currency in India
1. Technological Dependency: Digital currency in India relies heavily on technology infrastructure and connectivity. In areas with limited access to reliable internet or technological resources, individuals may face difficulties in adopting and utilizing digital currency effectively.
2. Cybersecurity Risks: Digital currency in India is susceptible to cybersecurity risks, including hacking, data breaches, and phishing attacks. Users must exercise caution and employ robust security measures to protect their digital wallets and personal information.
3. Lack of Physical Tangibility: Unlike traditional currency, digital currency in India lacks physical tangibility. Some individuals may find it challenging to trust and accept a currency that exists solely in digital form, leading to potential adoption barriers.
4. Volatility: Digital currencies, including cryptocurrencies, are known for their price volatility. Fluctuations in the value of digital currency in India can make it a risky medium of exchange or investment, potentially impacting individuals’ financial stability.
5. Limited Acceptance: While digital currency adoption is growing, it still has limited acceptance in mainstream businesses and establishments in India. This can hinder its widespread usage and convenience for everyday transactions.
6. Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory landscape surrounding digital currency in India is still evolving. Uncertainties and lack of clear guidelines from regulatory authorities may create confusion and hesitation among users and businesses.
7. Transaction Reversibility: Digital currency transactions are often irreversible once confirmed. In the event of fraudulent transactions or accidental transfers, recovering funds can be challenging, unlike traditional banking systems where dispute resolution mechanisms exist.
8. Technical Complexity: Digital currency in India may require individuals to understand and navigate technical concepts, such as digital wallets, private keys, and blockchain technology. This can be a barrier for users who are less technologically inclined or unfamiliar with these concepts.
9. Energy Consumption: Some digital currencies, especially cryptocurrencies, require significant computational power and energy consumption for mining and transaction verification. This energy-intensive process can have environmental implications and contribute to carbon footprints.
10. Potential for Illicit Activities: Digital currency in India, like any financial system, can be exploited for illicit activities, such as money laundering and illegal transactions. The pseudonymous nature of certain digital currencies may pose challenges in identifying and preventing such activities.
Countries that have issued CBDC
Currently, very few countries launched CBDC but many more are on the Concept and Research level, you will find hundreds of CDBC launched in 2023. The following countries have issued CBDC:
| Country / Region | Central Bank(s) | Announcement Year | Status |
| Bahamas | Central Bank of Bahamas | 2022 | Launched |
| Jamaica | Bank of Jamaica | 2022 | Launched |
| Singapore | Monetary Authority of Singapore | 2022 | Pilot |
| India | Reserve Bank of India | 2022 | Pilot |
| France | Banque de France | 2022 | Pilot |
| China | People’s Bank of China | 2022 | Pilot |
| Nigeria | Central Bank of Nigeria | 2022 | Pilot |
| France | Banque de France | 2022 | Pilot |
| Eastern Caribbean Economic and Currency Union | Eastern Caribbean Central Bank (ECCB) | 2022 | Pilot |
Digital Payment Journey of India
| Digital Payment Products | Year of Launch |
| Credit Card | 1981 |
| ATM | 1987 |
| ECS | 1990 |
| Online Banking Service (ICICI Bank) | 1996 |
| Bill Desk Payment Gateway | 1999 |
| RTGS | 2004 |
| NEFT | 2005 |
| IMPS | 2010 |
| RuPay Card | 2012 |
| UPI | 2016 |
| NACH | 2020 |
| CBDC | 2022 |
Conclusion
Digital currency in India is offering a range of advantages and opportunities for individuals and businesses. As the country embraces the digital revolution, digital currency in India has the potential to enhance financial inclusion, streamline transactions, increase transparency, and foster innovation. However, it is essential to address the challenges and disadvantages associated with digital currency, such as technological dependency, cybersecurity risks, and regulatory uncertainties.
By implementing robust security measures, promoting awareness, and establishing clear regulations, India can harness the full potential of digital currency, paving the way for a more inclusive, efficient, and secure financial ecosystem. As the journey towards a digital future unfolds, digital currency in India is set to play a significant role in shaping the country’s economy, empowering individuals, and driving technological innovation. With careful consideration and continued progress, digital currency in India holds the promise of a transformative financial landscape that benefits all.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How to buy Digital Currency in India?
Eight banks have been identified for the first phase of this pilot project. The first phase will begin with four banks, via the State Bank of India, ICICI Bank, Yes Bank, and IDFC First Bank in four cities across the country; these banks will issue Digital Currency to their customers on request.
Q2: Can digital currency be converted to cash?
Yes, you can deposit it in your account and withdraw cash from your account, in some time the facility of exchanging Digital Currency will be available.
Q3: What is the price of the digital rupee?
No additional cost for issuing Digital Currency, its value is the same as physical notes.
Q4: Is digital currency legal?
Yes, Digital Currency is legal tender like physical cash.
Q5: Who is the owner of digital currency?
The Reserve Bank of India is issuing Digital currency and the owner of the Digital Currency of India is the Bearer of this currency. You can get the same value of money if you want to return it.



